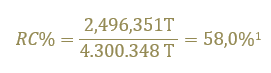Background
One of the objectives of the steel for packaging industry is to meet the requirements for safe and efficient packaging of food, beverages and other products in a responsible manner.
To meet this objective, the European steel for packaging industry has cooperated for decades to close the recycling loop in Europe. Steel, a permanent material, is the most recycled material in the world. In Europe, 85.5% of steel packaging is recycled making it the most recycled material for food, beverage and other household packaging.
Steel is fully recyclable. In substitution of raw materials, steel scrap forms part of a new steel production process. Consequently, every steel plant is in fact a recycling plant, which contributes to increasing the recycling rate of steel packaging.
The steel packaging supply chain does recognise that both recycling rate and recycled content are used in the packaging industry for defining the environmental performance of packaging material in general. For this reason, we are often asked about the recycled content of steel for packaging that is supplied by European tinplate producers.
Given this fact the industry has always focused on closing the loop for steel packaging to ensure the material is used over and over again in new cycles. We therefore have developed a coherent approach that gives insight into the amount of recycled scrap that is used to produce the total volume of steel for packaging in Europe.
Goal and scope
This formula is used by our industry to calculate comparable recycled content numbers for steel for packaging that can be used by the stakeholders to benchmark steel for packaging in Europe against other packaging materials.
Formula
Recycled content (RC) in EU for steel for packaging =
Total steel for packaging scrap consumption / Total steel for packaging production
[1] APEAL (data 2017, certified by CE Delft and validated by the European Commission in 2020)